Server Sempurna - Fedora 15 x86_64 [ISPConfig 3]
Tutorial ini menunjukkan cara menyiapkan server Fedora 15 (x86_64) untuk instalasi ISPConfig 3, dan cara menginstal ISPConfig 3. ISPConfig 3 adalah panel kontrol webhosting yang memungkinkan Anda untuk mengonfigurasi layanan berikut melalui browser web:Server web Apache , Server email Postfix, MySQL, server nama BIND, PureFTPd, SpamAssassin, ClamAV, dan banyak lagi.
Harap perhatikan bahwa pengaturan ini tidak berfungsi untuk ISPConfig 2 ! Ini hanya berlaku untuk ISPConfig 3!
Saya tidak memberikan jaminan apa pun bahwa ini akan berhasil untuk Anda!
Panduan ISPConfig 3
Untuk mempelajari cara menggunakan ISPConfig 3, saya sangat menyarankan untuk mengunduh Manual ISPConfig 3.
Pada sekitar 300 halaman, ini mencakup konsep di balik ISPConfig (admin, reseller, klien), menjelaskan cara menginstal dan memperbarui ISPConfig 3, menyertakan referensi untuk semua formulir dan bidang formulir di ISPConfig bersama dengan contoh input yang valid, dan memberikan tutorial untuk tugas paling umum di ISPConfig 3. Ini juga menjelaskan cara membuat server Anda lebih aman dan dilengkapi dengan bagian pemecahan masalah di bagian akhir.
Aplikasi Monitor ISPConfig Untuk Android
Dengan Aplikasi Monitor ISPConfig, Anda dapat memeriksa status server Anda dan mengetahui apakah semua layanan berjalan seperti yang diharapkan. Anda dapat memeriksa port TCP dan UDP dan melakukan ping ke server Anda. Selain itu, Anda dapat menggunakan aplikasi ini untuk meminta detail dari server yang telah menginstal ISPConfig (harap diperhatikan bahwa versi ISPConfig 3 yang diinstal minimum dengan dukungan untuk Aplikasi ISPConfig Monitor adalah 3.0.3.3! ); detail ini mencakup semua yang Anda ketahui dari modul Monitor di ISPConfig Control Panel (misalnya layanan, log email dan sistem, antrian email, info CPU dan memori, penggunaan disk, kuota, detail OS, log RKHunter, dll.), dan tentu saja , karena ISPConfig berkemampuan multiserver, Anda dapat memeriksa semua server yang dikendalikan dari server master ISPConfig Anda.
Untuk mengunduh dan petunjuk penggunaan, silakan kunjungi http://www.ispconfig.org/ispconfig-3/ispconfig-monitor-app-for-android/.
1 Persyaratan
Untuk menginstal sistem seperti itu, Anda memerlukan yang berikut:
- Unduh gambar iso DVD Fedora 15 dari cermin di dekat Anda (daftar cermin dapat ditemukan di sini:http://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/publiclist/Fedora/15/), mis. http://ftp.tu-chemnitz.de/pub/linux/fedora/linux/releases/15/Fedora/x86_64/iso/Fedora-15-x86_64-DVD.iso
- koneksi internet...
2 Catatan Awal
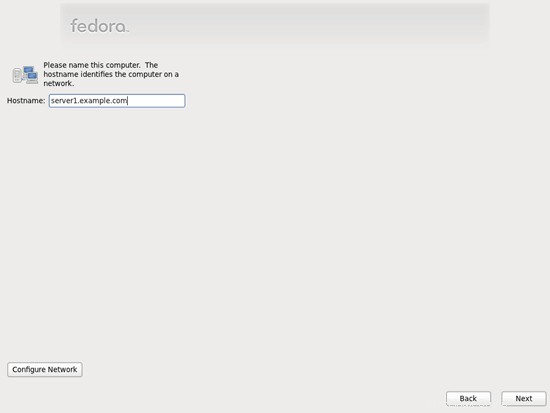
Dalam tutorial ini saya menggunakan hostname server1.example.com dengan alamat IP 192.168.0.100 dan gateway 192.168.0.1. Setelan ini mungkin berbeda untuk Anda, jadi Anda harus menggantinya jika perlu.
Harap pastikan bahwa sistem yang ingin Anda tingkatkan memiliki lebih dari 600 MB RAM - jika tidak, sistem akan hang saat mencoba melakukan boot dengan pesan berikut:
Trying to unpack rootfs image as initramfs...
3 Instal Sistem Dasar
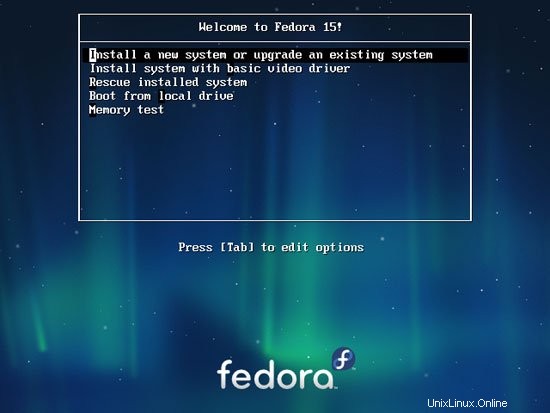
Boot dari DVD Fedora 15 Anda. Pilih Instal sistem baru atau perbarui sistem yang ada:
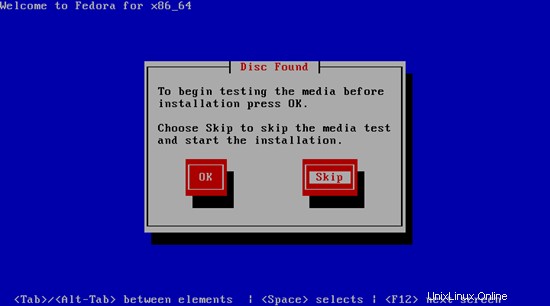
Diperlukan waktu lama untuk menguji media penginstalan, jadi kami melewatkan tes ini di sini:
Pilih bahasa Anda selanjutnya:
Pilih tata letak keyboard Anda:
Saya berasumsi bahwa Anda menggunakan hard drive yang terpasang secara lokal, jadi Anda harus memilih Perangkat Penyimpanan Dasar di sini:
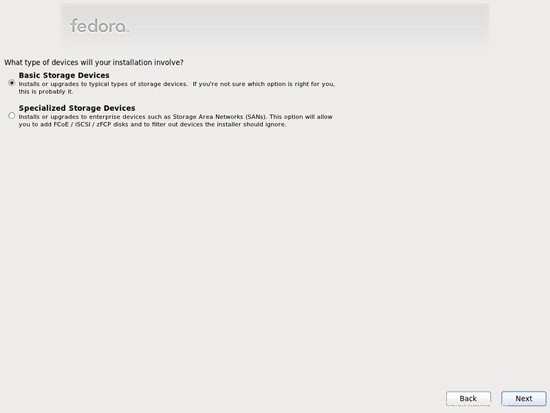
Karena kami menginginkan instalasi Fedora baru, klik tombol Ya, buang data apa pun berikutnya:
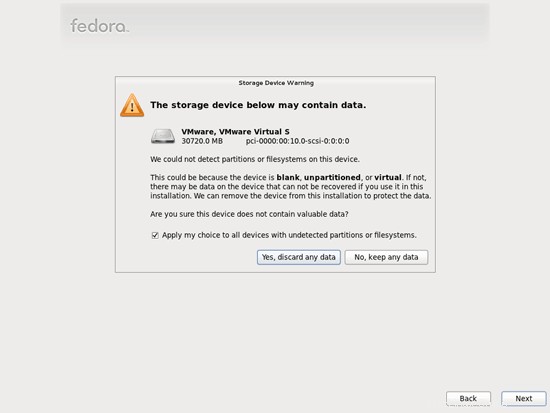
Isi nama host server:
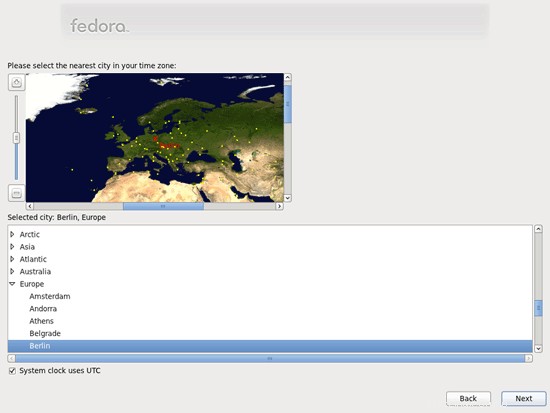
Pilih zona waktu Anda:

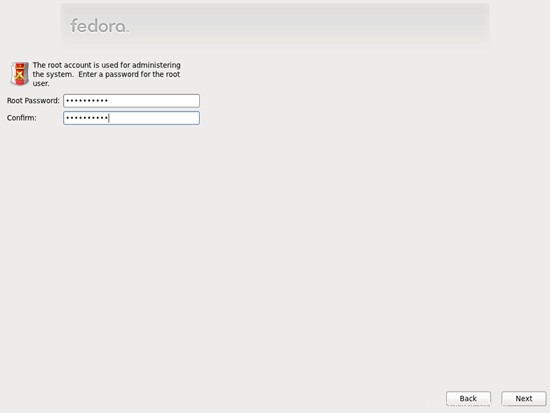
Berikan root kata sandi:
Selanjutnya kita melakukan partisi. Pilih Ganti Sistem Linux yang Ada. Ini akan memberi Anda partisi /boot kecil dan partisi / besar yang baik untuk tujuan kita:
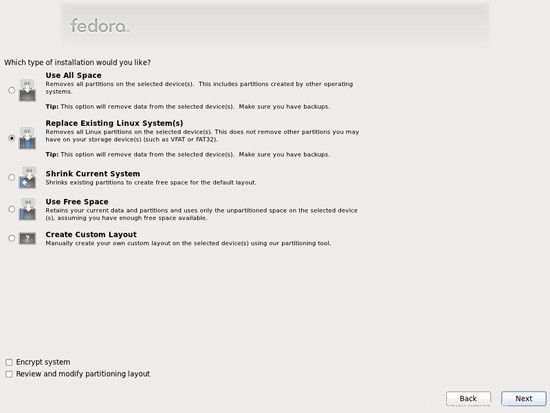
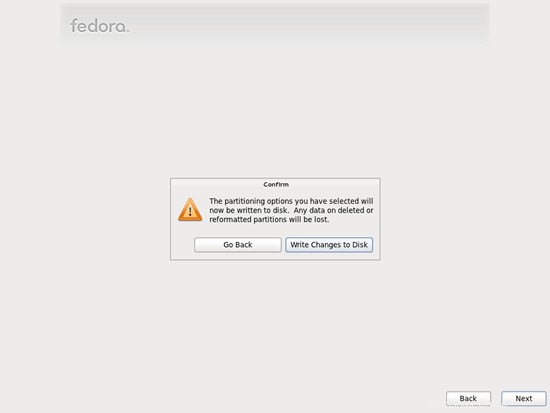
Pilih Tulis Perubahan ke Disk:
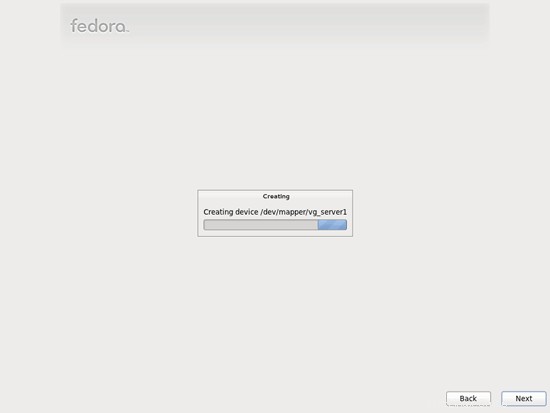
Hard drive sedang diformat:
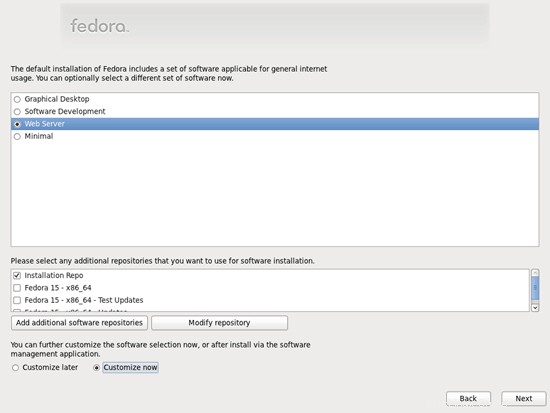
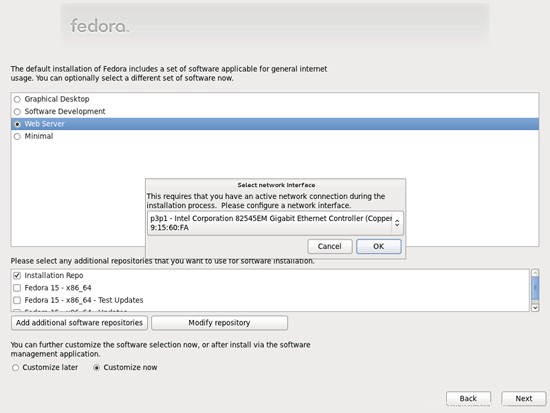
Sekarang kita pilih perangkat lunak yang ingin kita instal. Hapus centang Graphical Desktop dan periksa Server Web sebagai gantinya. Kemudian centang Sesuaikan sekarang. Setelah itu, pilih repositori tambahan Fedora 15 - x86_64 dan Fedora 15 - x86_64 - Pembaruan (jika Anda menggunakan sistem i686, namanya mungkin Fedora 15 - i686 dan Fedora 15 - i686 - Pembaruan):

Karena dua repositori terakhir memerlukan koneksi Internet, sebuah jendela baru akan muncul di mana Anda harus mengonfigurasi kartu jaringan Anda. Pilih kartu jaringan Anda dan klik OK:
Server Sempurna - Fedora 15 x86_64 [ISPConfig 3] - Halaman 2
4 Ubah Nama NIC Anda Menjadi ethx
Sekarang kita harus mengkonfigurasi Fedora untuk tidak menggunakan nama perangkat BIOS untuk antarmuka jaringan kita lagi. Alih-alih p3p1, kita membutuhkan eth0 lama kita yang baik kembali (karena jika tidak, firewall ISPConfig akan menjadi gila dan memblokir semuanya karena mengharapkan eth0 alih-alih p3p1). Buka /etc/grub.conf...
vi /etc/grub.conf
... dan tambahkan biosdevname=0 ke baris kernel:
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.
# root (hd0,0)
# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/mapper/vg_server1-lv_root
# initrd /initrd-[generic-]version.img
#boot=/dev/sda
default=0
timeout=0
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz
hiddenmenu
title Fedora (2.6.38.6-27.fc15.x86_64)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.38.6-27.fc15.x86_64 ro root=/dev/mapper/vg_server1-lv_root rd_LVM_LV=vg_server1/lv_root rd_LVM_LV=vg_server1/lv_swap rd_NO_LUKS rd_NO_MD rd_NO_DM LANG=en_US.UTF-8 SYSFONT=latarcyrheb-sun16 KEYTABLE=de rhgb quiet biosdevname=0
initrd /initramfs-2.6.38.6-27.fc15.x86_64.img |
Kemudian reboot sistem:
reboot
Setelah reboot, NIC Anda akan diberi nama eth0. Jalankan...
ifconfig
... untuk memverifikasi:
[example@unixlinux.online ~]# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:15:60:FA
inet addr:192.168.0.100 Bcast:192.168.0.255.255.255.255 255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe15:60fa/64 Cakupan:Link
UP BROADCAST MENJALANKAN MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metrik:1
jatuh 0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:58 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes byte:9682 (9.4 KiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: :pe Host
UP LOOPBACK MENJALANKAN MTU:16436 Metrik:1
Paket RX:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
runped error:0 paket:2 jatuh 0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX byte:100 (100.0 b) TX byte:100 (100.0 b)
[example@unixlinux.online ~]#
5 Sesuaikan /etc/hosts
Selanjutnya kita edit /etc/hosts. Jadikan seperti ini:
vi /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 192.168.0.100 server1.example.com server1 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 |
Anda harus menambahkan baris untuk server1.example.com dan menghapus server1.example.com dan server1 dari baris 127.0.0.1.
6 Konfigurasi Firewall
(Anda dapat melewati bab ini jika Anda telah menonaktifkan firewall di akhir penginstalan sistem dasar.)
Saya ingin menginstal ISPConfig di akhir tutorial ini yang dilengkapi dengan firewallnya sendiri. Itu sebabnya saya menonaktifkan firewall Fedora default sekarang. Tentu saja, Anda bebas untuk membiarkannya dan mengonfigurasinya sesuai kebutuhan Anda (tetapi Anda tidak boleh menggunakan firewall lain di kemudian hari karena kemungkinan besar akan mengganggu firewall Fedora).
Jalankan
system-config-firewall
dan menonaktifkan firewall.
Untuk memeriksa apakah firewall benar-benar telah dinonaktifkan, Anda dapat menjalankan
iptables -L
setelah itu. Outputnya akan terlihat seperti ini:
[example@unixlinux.online ~]# iptables -L
Rantai INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source tujuan
Rantai FORWARD (
Keluaran rantai (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt sumber tujuan
[example@unixlinux]#
7 Nonaktifkan SELinux
SELinux adalah ekstensi keamanan Fedora yang seharusnya memberikan keamanan yang diperluas. Menurut pendapat saya Anda tidak memerlukannya untuk mengkonfigurasi sistem yang aman, dan biasanya menyebabkan lebih banyak masalah daripada keuntungan (pikirkan setelah Anda melakukan pemecahan masalah selama seminggu karena beberapa layanan tidak berfungsi seperti yang diharapkan, dan kemudian Anda mengetahui bahwa semuanya baik-baik saja, hanya SELinux yang menyebabkan masalah). Oleh karena itu saya menonaktifkannya (ini adalah suatu keharusan jika Anda ingin menginstal ISPConfig nanti).
Edit /etc/selinux/config dan atur SELINUX=disabled:
vi /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted |
Setelah itu kita harus me-reboot sistem:
reboot
8 Instal Beberapa Perangkat Lunak
Pertama kita mengimpor kunci GPG untuk paket perangkat lunak:
rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY*
Selanjutnya kita update paket-paket yang sudah ada di sistem:
yum update
Sekarang kita install beberapa paket software yang dibutuhkan nantinya:
yum groupinstall 'Development Tools'
yum groupinstall 'Development Libraries'
9 Kuota Jurnal
(Jika Anda telah memilih skema partisi yang berbeda dari saya, Anda harus menyesuaikan bab ini sehingga kuota berlaku untuk partisi yang Anda butuhkan.)
Untuk memasang kuota, kita jalankan perintah ini:
yum install quota
Edit /etc/fstab dan tambahkan ,usrjquota=aquota.user,grpjquota=aquota.group,jqfmt=vfsv0 ke partisi / (/dev/mapper/vg_server1-lv_root):
vi /etc/fstab
# # /etc/fstab # Created by anaconda on Wed May 25 15:57:24 2011 # # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk' # See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info # /dev/mapper/vg_server1-lv_root / ext4 defaults,usrjquota=aquota.user,grpjquota=aquota.group,jqfmt=vfsv0 1 1 UUID=366ba6a7-7e68-4ec9-9743-4b02dd105180 /boot ext4 defaults 1 2 /dev/mapper/vg_server1-lv_swap swap swap defaults 0 0 tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0 devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0 proc /proc proc defaults 0 0 |
Kemudian jalankan
mount -o remount /
quotacheck -avugm
quotaon -avug
untuk mengaktifkan kuota.
10 Instal Apache, MySQL, phpMyAdmin
Ini semua dapat diinstal dengan satu perintah:
yum install ntp httpd mysql-server php php-mysql php-mbstring php-mcrypt phpMyAdmin
Server Sempurna - Fedora 15 x86_64 [ISPConfig 3] - Halaman 4
11 Instal Courier-IMAP, Courier-Authlib, Dan Maildrop
Sayangnya tidak ada paket rpm untuk Courier-IMAP, Courier-Authlib, dan Maildrop, oleh karena itu kami harus membuatnya sendiri.
Hapus dulu Dovecot (Fedora 15 hadir dengan Dovecot 2.x; sayangnya, ISPConfig 3 mendukung Dovecot 1.2.x, tetapi tidak 2.x):
yum remove dovecot dovecot-mysql
Kemudian install prasyarat yang kita perlukan untuk membangun paket Courier rpm:
yum install rpm-build gcc mysql-devel openssl-devel cyrus-sasl-devel pkgconfig zlib-devel pcre-devel openldap-devel postgresql-devel expect libtool-ltdl-devel openldap-servers libtool gdbm-devel pam-devel gamin-devel libidn-devel
Paket RPM tidak boleh dibangun sebagai root; kurir-imap bahkan akan menolak untuk mengkompilasi jika mendeteksi bahwa kompilasi dijalankan sebagai pengguna root. Oleh karena itu kami membuat akun pengguna normal sekarang (falko dalam contoh ini) dan memberinya kata sandi:
useradd -m -s /bin/bash falko
passwd falko
Kita akan membutuhkan perintah sudo nanti agar falko pengguna dapat mengkompilasi dan menginstal paket rpm. Tapi pertama-tama, kita harus mengizinkan falko untuk menjalankan semua perintah menggunakan sudo:
Jalankan
visudo
Di file yang terbuka ada baris root ALL=(ALL) ALL. Tambahkan baris serupa untuk falko tepat di bawah baris itu:
[...] ## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL falko ALL=(ALL) ALL [...] |
Sekarang kita siap untuk membangun paket rpm kita. Pertama menjadi pengguna falko:
su falko
Selanjutnya kita buat lingkungan build kita:
mkdir $HOME/rpm
mkdir $HOME/rpm/SOURCES
mkdir $HOME/rpm/SPECS
mkdir $HOME/rpm/BUILD
mkdir $HOME/rpm/BUILDROOT
mkdir $HOME/rpm/SRPMS
mkdir $HOME/rpm/RPMS
mkdir $HOME/rpm/RPMS/i386
mkdir $HOME/rpm/RPMS/x86_64
echo "%_topdir $HOME/rpm" >> $HOME/.rpmmacros
Sekarang kita membuat direktori unduhan dan mengunduh file sumber dari http://www.courier-mta.org/download.php:
mkdir $HOME/downloads
cd $HOME/downloads
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/courier/files/authlib/0.63.0/courier-authlib-0.63.0.tar.bz2/download
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/courier /files/imap/4.8.1/courier-imap-4.8.1.tar.bz2/download
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/courier/files/maildrop/2.5.4/maildrop-2.5 .4.tar.bz2/download
(Anda mungkin bertanya-tanya mengapa saya tidak mengunduh versi terbaru dari kurir-imap - 4.9.3 pada saat penulisan ini - tetapi gunakan yang lebih lama - 4.8.1. Ini karena 4.9.3 gagal dibangun di sistem saya , sedangkan 4.8.1 berfungsi dengan baik.)
Sekarang (masih dalam $HOME/downloads) kita dapat membangun authlib-kurir:
sudo rpmbuild -ta courier-authlib-0.63.0.tar.bz2
Setelah proses build, paket rpm dapat ditemukan di /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 (/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/i686 jika Anda menggunakan sistem i686). Perintah
sudo ls -l /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
menunjukkan kepada Anda paket rpm yang tersedia:
[example@unixlinux.online downloads]$ sudo ls -l /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
total 520
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 123448 Mei 25 18:06 kurir -authlib-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 265144 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-debuginfo-0.63.0-1.fc15. x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 34876 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-devel-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r --r-- 1 root root 17448 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-ldap-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13808 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-mysql-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13020 25 Mei 18:06 courier-authlib-pgsql-0.63. 0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8276 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-pipe-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 34108 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-userdb-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
[example@unixlinux.online downloads]$
Pilih yang ingin Anda instal, dan instal seperti ini:
sudo rpm -ivh /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/courier-authlib-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/courier-authlib-mysql-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/courier-authlib-devel-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
Sekarang kita kembali ke direktori unduhan kita:
cd $HOME/downloads
Jalankan perintah berikut untuk membuat direktori yang diperlukan/mengubah izin direktori (karena jika tidak, proses pembuatan untuk Courier-Imap akan gagal):
sudo mkdir /var/cache/ccache/tmp
sudo chmod o+rwx /var/cache/ccache/
sudo chmod 777 /var/cache/ccache/tmp
Sekarang jalankan rpmbuild lagi, kali ini tanpa sudo, jika tidak, kompilasi akan gagal karena dijalankan sebagai root:
rpmbuild -ta courier-imap-4.8.1.tar.bz2
Setelah proses pembuatan, paket rpm dapat ditemukan di $HOME/rpm/RPMS/x86_64 ($HOME/rpm/RPMS/i686 jika Anda menggunakan sistem i686):
cd $HOME/rpm/RPMS/x86_64
Perintah
ls -l
menunjukkan kepada Anda paket rpm yang tersedia:
[example@unixlinux.online x86_64]$ ls -l
total 1708
-rw-rw-r-- 1 falko falko 596432 Mei 25 18:33 courier-imap-4.8.1-2.15.x86_64 .rpm
-rw-rw-r-- 1 falko falko 1149328 Mei 25 18:33 courier-imap-debuginfo-4.8.1-2.15.x86_64.rpm
[example@unixlinux.online x86_64] $
Anda dapat menginstal kurir-imap seperti ini:
sudo rpm -ivh courier-imap-4.8.1-2.15.x86_64.rpm
Sekarang kita kembali ke direktori unduhan kita:
cd $HOME/downloads
dan jalankan rpmbuild lagi, kali ini untuk membuat paket maildrop:
sudo rpmbuild -ta maildrop-2.5.4.tar.bz2
Setelah proses build, paket rpm dapat ditemukan di /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 (/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/i686 jika Anda menggunakan sistem i686). Perintah
sudo ls -l /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
menunjukkan kepada Anda paket rpm yang tersedia:
[example@unixlinux.online downloads]$ sudo ls -l /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
total 1628
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 123448 Mei 25 18:06 kurir -authlib-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 265144 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-debuginfo-0.63.0-1.fc15. x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 34876 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-devel-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r --r-- 1 root root 17448 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-ldap-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13808 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-mysql-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13020 25 Mei 18:06 courier-authlib-pgsql-0.63. 0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8276 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-pipe-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 34108 Mei 25 18:06 courier-authlib-userdb-0.63.0-1.fc15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 278520 Mei 25 18:50 maildrop-2.5.4-1.15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 685672 Mei 25 18:50 maildrop-debuginfo-2.5.4 -1.15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 99924 Mei 25 18:50 maildrop-devel-2.5.4-1.15.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r- -r-- 1 root root 63968 Mei 25 18:50 maildrop-man-2.5.4-1.15.x86_64.rpm
[example@unixlinux.online downloads]$
Sekarang Anda dapat menginstal maildrop seperti ini:
sudo rpm -ivh /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/maildrop-2.5.4-1.15.x86_64.rpm
Setelah Anda mengkompilasi dan menginstal semua paket yang dibutuhkan, Anda dapat menjadi root kembali dengan mengetik
exit
12 Instal Postfix
Postfix dapat diinstal sebagai berikut:
yum install postfix
Kemudian matikan Sendmail dan mulai Postfix dan MySQL:
chkconfig --levels 235 mysqld pada
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
chkconfig sendmail mati
chkconfig --levels 235 postfix aktif
/etc/init.d/sendmail stop
/etc/init.d/postfix start
13 Instal Getmail
Getmail dapat diinstal sebagai berikut:
yum install getmail
14 Mengatur Kata Sandi MySQL Dan Konfigurasi phpMyAdmin
Setel kata sandi untuk akun root MySQL:
mysql_secure_installation
[example@unixlinux.online ~]# mysql_secure_installation
CATATAN:MENJALANKAN SEMUA BAGIAN SKRIP INI DIREKOMENDASIKAN UNTUK SEMUA MySQL
SERVER DI PRODUKSI MENGGUNAKAN! HARAP BACA SETIAP LANGKAH DENGAN SEKSAMA!
Untuk masuk ke MySQL guna mengamankannya, kami memerlukan kata sandi
saat ini untuk pengguna root. Jika Anda baru menginstal MySQL, dan
belum menyetel sandi root, sandi akan kosong,
jadi Anda cukup tekan enter di sini.
Enter sandi saat ini untuk root (masukkan untuk none): <-- ENTER
Oke, sandi berhasil digunakan, pindah ...
Menyetel sandi root memastikan bahwa tidak ada yang dapat masuk ke MySQL
root pengguna tanpa otorisasi yang benar.
Tetapkan sandi root? [Y/n] <-- ENTER
Sandi baru: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
Masukkan kembali sandi baru: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
Sandi berhasil diperbarui!
Memuat ulang tabel hak istimewa. .
... Berhasil!
Secara default, penginstalan MySQL memiliki pengguna anonim yang memungkinkan siapa saja
masuk ke MySQL tanpa harus memiliki akun pengguna dibuat untuk
mereka. Ini dimaksudkan hanya untuk pengujian, dan untuk membuat pemasangan
menjadi sedikit lebih lancar. Anda harus menghapusnya sebelum berpindah ke
lingkungan produksi.
Hapus pengguna anonim? [Y/n] <-- ENTER
... Berhasil!
Biasanya, root hanya diizinkan untuk terhubung dari 'localhost'. Ini
memastikan bahwa seseorang tidak dapat menebak kata sandi root dari jaringan.
Larang login root dari jarak jauh? [Y/n] <-- ENTER
... Berhasil!
Secara default, MySQL dilengkapi dengan database bernama 'test' yang dapat diakses oleh siapa saja
. Ini juga ditujukan hanya untuk pengujian, dan harus dihapus
sebelum dipindahkan ke lingkungan produksi.
Hapus database pengujian dan akses ke sana? [Y/n] <-- MASUKKAN
- Menghapus basis data pengujian...
... Berhasil!
- Menghapus hak istimewa pada basis data pengujian...
... Berhasil !
Memuat ulang tabel hak istimewa akan memastikan bahwa semua perubahan yang dibuat sejauh ini
akan segera berlaku.
Muat ulang tabel hak istimewa sekarang? [Y/n] <-- ENTER
... Berhasil!
Membersihkan...
Selesai! Jika Anda telah menyelesaikan semua langkah di atas, penginstalan MySQL
Anda seharusnya kini aman.
Terima kasih telah menggunakan MySQL!
[contoh @unixlinux.online ~]#
Sekarang kita mengkonfigurasi phpMyAdmin. Kami mengubah konfigurasi Apache sehingga phpMyAdmin mengizinkan koneksi tidak hanya dari localhost (dengan mengomentari bait
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
# phpMyAdmin - Web based MySQL browser written in php
#
# Allows only localhost by default
#
# But allowing phpMyAdmin to anyone other than localhost should be considered
# dangerous unless properly secured by SSL
Alias /phpMyAdmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
#<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/>
# Order Deny,Allow
# Deny from All
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
#</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/setup/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from 127.0.0.1
Allow from ::1
</Directory>
# These directories do not require access over HTTP - taken from the original
# phpMyAdmin upstream tarball
#
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/libraries/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from None
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/setup/lib/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from None
</Directory>
# This configuration prevents mod_security at phpMyAdmin directories from
# filtering SQL etc. This may break your mod_security implementation.
#
#<IfModule mod_security.c>
# <Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/>
# SecRuleInheritance Off
# </Directory>
#</IfModule> |
Kemudian kami membuat tautan startup sistem untuk Apache dan memulainya:
chkconfig --levels 235 httpd pada
/etc/init.d/httpd start
Sekarang Anda dapat mengarahkan browser Anda ke http://server1.example.com/phpmyadmin/ atau http://192.168.0.100/phpmyadmin/ dan masuk dengan nama pengguna root dan kata sandi MySQL root Anda yang baru.
Server Sempurna - Fedora 15 x86_64 [ISPConfig 3] - Halaman 5
15 Instal Amavisd-new, SpamAssassin Dan ClamAV
Untuk menginstal amavisd-new, spamassassin dan clamav, jalankan perintah berikut:
yum install amavisd-new spamassassin clamav clamav-data clamav-server clamav-update unzip bzip2 perl-DBD-mysql
Saat kami menginstal ClamAV, tugas cron terinstal yang mencoba memperbarui basis data virus ClamAV setiap tiga jam. Tetapi ini hanya berfungsi jika kita mengaktifkannya di /etc/sysconfig/freshclam dan /etc/freshclam.conf:
vi /etc/sysconfig/freshclam
Komentari baris FRESHCLAM_DELAY di akhir:
## When changing the periodicity of freshclam runs in the crontab, ## this value must be adjusted also. Its value is the timespan between ## two subsequent freshclam runs in minutes. E.g. for the default ## ## | 0 */3 * * * ... ## ## crontab line, the value is 180 (minutes). # FRESHCLAM_MOD= ## A predefined value for the delay in seconds. By default, the value is ## calculated by the 'hostid' program. This predefined value guarantees ## constant timespans of 3 hours between two subsequent freshclam runs. ## ## This option accepts two special values: ## 'disabled-warn' ... disables the automatic freshclam update and ## gives out a warning ## 'disabled' ... disables the automatic freshclam silently # FRESHCLAM_DELAY= ### !!!!! REMOVE ME !!!!!! ### REMOVE ME: By default, the freshclam update is disabled to avoid ### REMOVE ME: network access without prior activation #FRESHCLAM_DELAY=disabled-warn # REMOVE ME |
vi /etc/freshclam.conf
Beri komentar pada baris Contoh:
[...] # Comment or remove the line below. #Example [...] |
Kemudian kita mulai freshclam, amavisd, dan clamd...
sa-update
chkconfig --levels 235 amavisd aktif
chkconfig --levels 235 clamd.amavisd aktif
/usr/bin/freshclam
/etc/init.d/amavisd start
/etc/init.d/clamd.amavisd start
Selanjutnya lakukan ini:
rm -f /var/spool/amavisd/clamd.sock
mkdir /var/run/clamav.amavisd /var/run/clamd.amavisd /var/run/amavisd
chown amavis /var/run /clamav.amavisd
chown amavis /var/run/clamd.amavisd
chown amavis /var/run/amavisd
ln -sf /var/spool/amavisd/clamd.sock /var/ run/clamav.amavisd/clamd.sock
ln -sf /var/spool/amavisd/clamd.sock /var/run/clamd.amavisd/clamd.sock
/etc/init.d/clamd .amavisd mulai ulang
Fedora 15 memiliki direktori /run untuk menyimpan data runtime. /run sekarang menjadi tmpfs, dan /var/run dan /var/lock sekarang diikat ke /run dan /run/lock dari tmpfs, dan karenanya dikosongkan saat reboot (lihat https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en -US/Fedora/15/html/Release_Notes/sect-Release_Notes-Changes_for_SysAdmin.html untuk detail lebih lanjut).
Artinya setelah reboot, direktori /var/run/clamav.amavisd, /var/run/clamd.amavisd, dan /var/run/amavisd yang baru saja kita buat tidak akan ada lagi, dan oleh karena itu clamd dan amavisd akan gagal untuk memulai. Oleh karena itu kami membuat file /etc/tmpfiles.d/amavisd.conf sekarang yang akan membuat direktori ini saat startup sistem (lihat http://0pointer.de/public/systemd-man/tmpfiles.d.html untuk lebih jelasnya):
vi /etc/tmpfiles.d/amavisd.conf
D /var/run/clamav.amavisd 0755 amavis root - D /var/run/clamd.amavisd 0755 amavis root - D /var/run/amavisd 0755 amavis root - |
16 Menginstal mod_php, mod_fcgi/PHP5, Dan suPHP
ISPConfig 3 memungkinkan Anda untuk menggunakan mod_php, mod_fcgi/PHP5, cgi/PHP5, dan suPHP per situs web.
Kita dapat menginstal Apache2 dengan mod_php5, mod_fcgid, dan PHP5 sebagai berikut:
yum install php php-devel php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-mysql php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mssql php-snmp php-soap php-tidy curl curl-devel perl-libwww-perl ImageMagick libxml2 libxml2-devel mod_fcgid php-cli httpd-devel
Selanjutnya kita buka /etc/php.ini...
vi /etc/php.ini
... dan ubah pelaporan kesalahan (agar pemberitahuan tidak ditampilkan lagi) dan batalkan komentar cgi.fix_pathinfo=1:
[...] ;error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE [...] ; cgi.fix_pathinfo provides *real* PATH_INFO/PATH_TRANSLATED support for CGI. PHP's ; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok ; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting ; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting ; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts ; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED. ; http://www.php.net/manual/en/ini.core.php#ini.cgi.fix-pathinfo cgi.fix_pathinfo=1 [...] |
Selanjutnya kita install suPHP:
cd /tmp
wget http://www.suphp.org/download/suphp-0.7.1.tar.gz
tar xvfz suphp-0.7.1.tar.gz
cd suphp-0.7.1/
./configure --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc --with-apr=/usr/bin/apr-1-config --with-apxs=/usr/sbin/apxs --with-apache-user=apache --with-setid-mode=owner --with-php=/usr/bin/php-cgi --with-logfile=/var/log/httpd/suphp_log --enable-SUPHP_USE_USERGROUP=yes
make
make install
Then we add the suPHP module to our Apache configuration...
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/suphp.conf
LoadModule suphp_module modules/mod_suphp.so |
... and create the file /etc/suphp.conf as follows:
vi /etc/suphp.conf
[global] ;Path to logfile logfile=/var/log/httpd/suphp.log ;Loglevel loglevel=info ;User Apache is running as webserver_user=apache ;Path all scripts have to be in docroot=/ ;Path to chroot() to before executing script ;chroot=/mychroot ; Security options allow_file_group_writeable=true allow_file_others_writeable=false allow_directory_group_writeable=true allow_directory_others_writeable=false ;Check wheter script is within DOCUMENT_ROOT check_vhost_docroot=true ;Send minor error messages to browser errors_to_browser=false ;PATH environment variable env_path=/bin:/usr/bin ;Umask to set, specify in octal notation umask=0077 ; Minimum UID min_uid=100 ; Minimum GID min_gid=100 [handlers] ;Handler for php-scripts x-httpd-suphp="php:/usr/bin/php-cgi" ;Handler for CGI-scripts x-suphp-cgi="execute:!self" |
Finally we restart Apache:
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
16.1 Ruby
Starting with version 3.0.3, ISPConfig 3 has built-in support for Ruby. Instead of using CGI/FastCGI, ISPConfig depends on mod_ruby being available in the server's Apache.
For Fedora 15, there's no mod_ruby package available, so we must compile it ourselves. First we install some prerequisites:
yum install ruby ruby-devel
Next we download and install mod_ruby as follows:
cd /tmp
wget http://modruby.net/archive/mod_ruby-1.3.0.tar.gz
tar zxvf mod_ruby-1.3.0.tar.gz
cd mod_ruby-1.3.0/
./configure.rb --with-apr-includes=/usr/include/apr-1
make
make install
Finally we must add the mod_ruby module to the Apache configuration, so we create the file /etc/httpd/conf.d/ruby.conf...
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/ruby.conf
LoadModule ruby_module modules/mod_ruby.so RubyAddPath /1.8 |
... and restart Apache:
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
(If you leave out the RubyAddPath /1.8 directive, you will see errors like the following ones in Apache's error log when you call Ruby files:
[Thu May 26 02:05:05 2011] [error] mod_ruby:ruby:0:in `require':no such file to load -- apache/ruby-run (LoadError)
[Thu May 26 02:05:05 2011] [error] mod_ruby:failed to require apache/ruby-run
[Thu May 26 02:05:05 2011] [error] mod_ruby:error in ruby
)
16.2 WebDAV
WebDAV should already be enabled, but to check this, open /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf and make sure that the following three modules are active:
vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[...] LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so [...] LoadModule dav_module modules/mod_dav.so [...] LoadModule dav_fs_module modules/mod_dav_fs.so [...] |
If you have to modify /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, don't forget to restart Apache afterwards:
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
17 Install PureFTPd
PureFTPd can be installed with the following command:
yum install pure-ftpd
Then create the system startup links and start PureFTPd:
chkconfig --levels 235 pure-ftpd on
/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd start
Now we configure PureFTPd to allow FTP and TLS sessions. FTP is a very insecure protocol because all passwords and all data are transferred in clear text. By using TLS, the whole communication can be encrypted, thus making FTP much more secure.
OpenSSL is needed by TLS; to install OpenSSL, we simply run:
yum install openssl
Open /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf...
vi /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf
If you want to allow FTP and TLS sessions, set TLS to 1:
[...] # This option can accept three values : # 0 : disable SSL/TLS encryption layer (default). # 1 : accept both traditional and encrypted sessions. # 2 : refuse connections that don't use SSL/TLS security mechanisms, # including anonymous sessions. # Do _not_ uncomment this blindly. Be sure that : # 1) Your server has been compiled with SSL/TLS support (--with-tls), # 2) A valid certificate is in place, # 3) Only compatible clients will log in. TLS 1 [...] |
In order to use TLS, we must create an SSL certificate. I create it in /etc/ssl/private/, therefore I create that directory first:
mkdir -p /etc/ssl/private/
Afterwards, we can generate the SSL certificate as follows:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 7300 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:<-- Enter your Country Name (e.g., "DE").
State or Province Name (full name) []:<-- Enter your State or Province Name.
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:<-- Enter your City.
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:<-- Enter your Organization Name (e.g., the name of your company).
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:<-- Enter your Organizational Unit Name (e.g. "IT Department").
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:<-- Enter the Fully Qualified Domain Name of the system (e.g. "server1.example.com").
Email Address []:<-- Enter your Email Address.
Change the permissions of the SSL certificate:
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
Finally restart PureFTPd:
/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd restart
That's it. You can now try to connect using your FTP client; however, you should configure your FTP client to use TLS.
18 Install BIND
We can install BIND as follows:
yum install bind bind-utils
Next open /etc/sysconfig/named...
vi /etc/sysconfig/named
... and comment out the ROOTDIR=/var/named/chroot line:
# BIND named process options # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ # Currently, you can use the following options: # # ROOTDIR="/var/named/chroot" -- will run named in a chroot environment. # you must set up the chroot environment # (install the bind-chroot package) before # doing this. # NOTE: # Those directories are automatically mounted to chroot if they are # empty in the ROOTDIR directory. It will simplify maintenance of your # chroot environment. # - /var/named # - /etc/pki/dnssec-keys # - /etc/named # - /usr/lib64/bind or /usr/lib/bind (architecture dependent) # # Those files are mounted as well if target file doesn't exist in # chroot. # - /etc/named.conf # - /etc/rndc.conf # - /etc/rndc.key # - /etc/named.rfc1912.zones # - /etc/named.dnssec.keys # - /etc/named.iscdlv.key # # Don't forget to add "$AddUnixListenSocket /var/named/chroot/dev/log" # line to your /etc/rsyslog.conf file. Otherwise your logging becomes # broken when rsyslogd daemon is restarted (due update, for example). # # OPTIONS="whatever" -- These additional options will be passed to named # at startup. Don't add -t here, use ROOTDIR instead. # # KEYTAB_FILE="/dir/file" -- Specify named service keytab file (for GSS-TSIG) # # DISABLE_ZONE_CHECKING -- By default, initscript calls named-checkzone # utility for every zone to ensure all zones are # valid before named starts. If you set this option # to 'yes' then initscript doesn't perform those # checks. #ROOTDIR=/var/named/chroot |
Then we create the startup links:
chkconfig --levels 235 named on
We don't start BIND now because it must be configured first - this will be done automatically by the ISPConfig 3 installer later on.
19 Install Vlogger, Webalizer, And AWStats
Vlogger, webalizer, and AWStats can be installed as follows:
yum install webalizer awstats perl-DateTime-Format-HTTP perl-DateTime-Format-Builder
cd /tmp
wget http://n0rp.chemlab.org/vlogger/vlogger-1.3.tar.gz
tar xvfz vlogger-1.3.tar.gz
mv vlogger-1.3/vlogger /usr/sbin/
rm -rf vlogger*
20 Install Jailkit
Jailkit is needed only if you want to chroot SSH users. It can be installed as follows (important:Jailkit must be installed before ISPConfig - it cannot be installed afterwards!):
cd /tmp
wget http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/jailkit-2.14.tar.gz
tar xvfz jailkit-2.14.tar.gz
cd jailkit-2.14
./configure
make
make install
cd ..
rm -rf jailkit-2.14*
21 Install fail2ban
This is optional but recommended, because the ISPConfig monitor tries to show the log:
yum install fail2ban
chkconfig --levels 235 fail2ban on
/etc/init.d/fail2ban start
22 Install rkhunter
rkhunter can be installed as follows:
yum install rkhunter
The Perfect Server - Fedora 15 x86_64 [ISPConfig 3] - Page 6
23 Install SquirrelMail
To install the SquirrelMail webmail client, run...
yum install squirrelmail
... and restart Apache:
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
Then configure SquirrelMail:
/usr/share/squirrelmail/config/conf.pl
We must tell SquirrelMail that we are using Courier-IMAP/-POP3:
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php (1.4.0)
---------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu --
1. Organization Preferences
2. Server Settings
3. Folder Defaults
4. General Options
5. Themes
6. Address Books
7. Message of the Day (MOTD)
8. Plugins
9. Database
10. Languages
D. Set pre-defined settings for specific IMAP servers
C Turn color off
S Save data
Q Quit
Command >> <-- D
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php
---------------------------------------------------------
While we have been building SquirrelMail, we have discovered some
preferences that work better with some servers that don't work so
well with others. If you select your IMAP server, this option will
set some pre-defined settings for that server.
Please note that you will still need to go through and make sure
everything is correct. This does not change everything. There are
only a few settings that this will change.
Please select your IMAP server:
bincimap = Binc IMAP server
courier = Courier IMAP server
cyrus = Cyrus IMAP server
dovecot = Dovecot Secure IMAP server
exchange = Microsoft Exchange IMAP server
hmailserver = hMailServer
macosx = Mac OS X Mailserver
mercury32 = Mercury/32
uw = University of Washington's IMAP server
gmail = IMAP access to Google mail (Gmail) accounts
quit = Do not change anything
Command >> <-- courier
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php
---------------------------------------------------------
While we have been building SquirrelMail, we have discovered some
preferences that work better with some servers that don't work so
well with others. If you select your IMAP server, this option will
set some pre-defined settings for that server.
Please note that you will still need to go through and make sure
everything is correct. This does not change everything. There are
only a few settings that this will change.
Please select your IMAP server:
bincimap = Binc IMAP server
courier = Courier IMAP server
cyrus = Cyrus IMAP server
dovecot = Dovecot Secure IMAP server
exchange = Microsoft Exchange IMAP server
hmailserver = hMailServer
macosx = Mac OS X Mailserver
mercury32 = Mercury/32
uw = University of Washington's IMAP server
gmail = IMAP access to Google mail (Gmail) accounts
quit = Do not change anything
Command >> courier
imap_server_type = courier
default_folder_prefix = INBOX.
trash_folder = Trash
sent_folder = Sent
draft_folder = Drafts
show_prefix_option = false
default_sub_of_inbox = false
show_contain_subfolders_option = false
optional_delimiter = .
delete_folder = true
Press any key to continue... <-- press ENTER
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php (1.4.0)
---------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu --
1. Organization Preferences
2. Server Settings
3. Folder Defaults
4. General Options
5. Themes
6. Address Books
7. Message of the Day (MOTD)
8. Plugins
9. Database
10. Languages
D. Set pre-defined settings for specific IMAP servers
C Turn color off
S Save data
Q Quit
Command >> <--S
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php (1.4.0)
---------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu --
1. Organization Preferences
2. Server Settings
3. Folder Defaults
4. General Options
5. Themes
6. Address Books
7. Message of the Day (MOTD)
8. Plugins
9. Database
10. Languages
D. Set pre-defined settings for specific IMAP servers
C Turn color off
S Save data
Q Quit
Command >> <--Q
One last thing we need to do is modify the file /etc/squirrelmail/config_local.php and comment out the $default_folder_prefix variable - if you don't do this, you will see the following error message in SquirrelMail after you've logged in:Query:CREATE "Sent" Reason Given:Invalid mailbox name.
vi /etc/squirrelmail/config_local.php
<?php /** * Local config overrides. * * You can override the config.php settings here. * Don't do it unless you know what you're doing. * Use standard PHP syntax, see config.php for examples. * * @copyright © 2002-2006 The SquirrelMail Project Team * @license http://opensource.org/licenses/gpl-license.php GNU Public License * @version $Id$ * @package squirrelmail * @subpackage config */ //$default_folder_prefix = ''; ?> |
Now you can type in http://server1.example.com/webmail or http://192.168.0.100/webmail in your browser to access SquirrelMail.
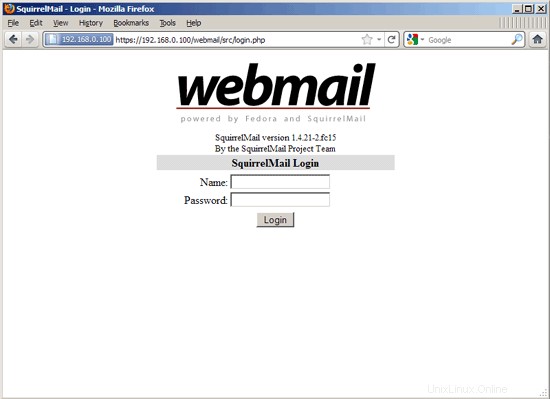
24 Install ISPConfig 3
To install ISPConfig 3 from the latest released version, do this:
cd /tmp
wget http://www.ispconfig.org/downloads/ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
tar xfz ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
cd ispconfig3_install /instal/
The next step is to run
php -q install.php
This will start the ISPConfig 3 installer:
[example@unixlinux.online install]# php -q install.php
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____ ___________ _____ __ _ ____
|_ _/ ___| _ \ / __ \ / _(_) /__ \
| | \ `--.| |_/ / | / \/ ___ _ __ | |_ _ __ _ _/ /
| | `--. \ __/ | | / _ \| '_ \| _| |/ _` | |_ |
_| |_/\__/ / | | \__/\ (_) | | | | | | | (_| | ___\ \
\___/\____/\_| \____/\___/|_| |_|_| |_|\__, | \____/
__/ |
|___/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>> Initial configuration
Operating System: Redhat or compatible, unknown version.
Following will be a few questions for primary configuration so be careful.
Default values are in [brackets] and can be accepted with
Tap in "quit" (without the quotes) to stop the installer.
Select language (en,de) [en]: <-- ENTER
Installation mode (standard,expert) [standard]: <-- ENTER
Full qualified hostname (FQDN) of the server, eg server1.domain.tld [server1.example.com]: <-- ENTER
MySQL server hostname [localhost]: <-- ENTER
MySQL root username [root]: <-- ENTER
MySQL root password []: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
MySQL database to create [dbispconfig]: <-- ENTER
MySQL charset [utf8]: <-- ENTER
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
......+++
...............+++
writing new private key to 'smtpd.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]: <-- ENTER
State or Province Name (full name) []: <-- ENTER
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]: <-- ENTER
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]: <-- ENTER
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: <-- ENTER
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []: <-- E NTER
Email Address []: <-- ENTER
Configuring Jailkit
Configuring SASL
Configuring PAM
Configuring Courier
Configuring Spamassassin
Configuring Amavisd
Configuring Getmail
Configuring Pureftpd
Configuring BIND
Configuring Apache
Configuring Vlogger
Configuring Apps vhost
Configuring Firewall
Installing ISPConfig
ISPConfig Port [8080]: <-- ENTER
Configuring DBServer
Installing ISPConfig crontab
no crontab for root
no crontab for getmail
Restarting services ...
Restarting mysqld (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Restarting postfix (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Restarting saslauthd (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Restarting amavisd (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Restarting clamd.amavisd (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Stopping Courier authentication services: authdaemond
Starting Courier authentication services: authdaemond
Stopping Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Starting Courier-IMAP server: imap generating-SSL-certificate... imap-ssl pop3 generating-SSL-certificate... pop3-ssl
Stopping Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Starting Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Stopping Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Starting Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Stopping Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Starting Courier-IMAP server: imap imap-ssl pop3 pop3-ssl
Restarting httpd (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Restarting pure-ftpd (via systemctl): [ OK ]
Installation completed.
[example@unixlinux.online install]#
Pemasang secara otomatis mengonfigurasi semua layanan yang mendasarinya, jadi tidak diperlukan konfigurasi manual.
Afterwards you can access ISPConfig 3 under http://server1.example.com:8080/ or http://192.168.0.100:8080/. Masuk dengan nama pengguna admin dan kata sandi admin (Anda harus mengubah kata sandi default setelah login pertama Anda):
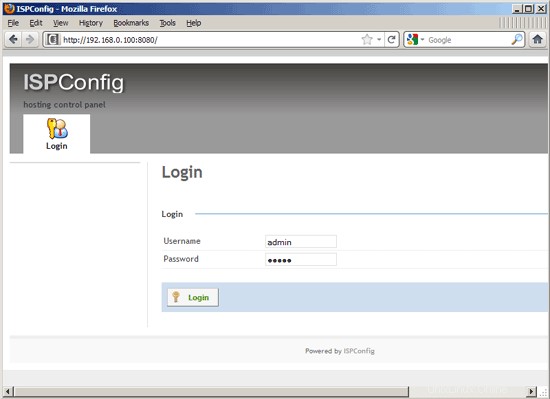
The system is now ready to be used.
24.1 ISPConfig 3 Manual
In order to learn how to use ISPConfig 3, I strongly recommend to download the ISPConfig 3 Manual.
On about 300 pages, it covers the concept behind ISPConfig (admin, resellers, clients), explains how to install and update ISPConfig 3, includes a reference for all forms and form fields in ISPConfig together with examples of valid inputs, and provides tutorials for the most common tasks in ISPConfig 3. It also lines out how to make your server more secure and comes with a troubleshooting section at the end.
24.2 ISPConfig Monitor App For Android
With the ISPConfig Monitor App, you can check your server status and find out if all services are running as expected. You can check TCP and UDP ports and ping your servers. In addition to that you can use this app to request details from servers that have ISPConfig installed (please note that the minimum installed ISPConfig 3 version with support for the ISPConfig Monitor App is 3.0.3.3! ); these details include everything you know from the Monitor module in the ISPConfig Control Panel (e.g. services, mail and system logs, mail queue, CPU and memory info, disk usage, quota, OS details, RKHunter log, etc.), and of course, as ISPConfig is multiserver-capable, you can check all servers that are controlled from your ISPConfig master server.
For download and usage instructions, please visit http://www.ispconfig.org/ispconfig-3/ispconfig-monitor-app-for-android/.
25 Links
- Fedora:http://fedoraproject.org/
- Network Device Naming:http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Features/ConsistentNetworkDeviceNaming
- /run directory:https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/Fedora/15/html/Release_Notes/sect-Release_Notes-Changes_for_SysAdmin.html
- tmpfiles.d:http://0pointer.de/public/systemd-man/tmpfiles.d.html
- ISPConfig:http://www.ispconfig.org/